
The healthcare system of India has undergone a crucial transformation due to technology advancement. With over a population of 1.4 billion , the healthcare system faces many challenges such as infrastructural gaps, lack of medical faculty.
1. Telemedicine: Bridging the Healthcare Access Gap

One of the most significant contributions of technology to India’s healthcare system has been the rise of telemedicine.
– Access to Specialists: Telemedicine allows patients in remote areas to consult with specialists and healthcare professionals located in urban centers. Through video consultations, patients can receive timely diagnoses, treatment plans, and follow-ups without the need to travel long distances.
– Pandemic Response: During the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine played a crucial role in maintaining healthcare services while minimizing physical contact. Government initiatives such as eSanjeevani, a national telemedicine service, facilitated millions of teleconsultations during the pandemic, ensuring continuity of care.
– Cost-Effective Healthcare: Telemedicine reduces healthcare costs by minimizing travel expenses for patients and improving efficiency for healthcare providers. It has also enabled more people to access quality care, thereby improving overall health outcomes.
2. AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing Diagnosis and Treatment
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming the way diseases are diagnosed and treated in India. These technologies enable healthcare providers to analyze large amounts of data quickly and accurately, leading to better clinical decision-making.
– Medical Imaging: AI-powered tools are improving the accuracy of diagnosing diseases such as cancer, tuberculosis, and heart conditions through medical imaging. By analyzing CT scans, X-rays, and MRIs, AI systems can detect abnormalities faster and more accurately than traditional methods, reducing the burden on radiologists.
– Predictive Analytics: AI is being used to predict disease outbreaks and patient outcomes based on historical data. This helps healthcare providers take preventive measures and allocate resources more efficiently. For example, AI-powered tools can predict the risk of complications in diabetic patients, allowing for timely interventions.
– Personalized Medicine: AI and ML are enabling personalized treatment plans based on an individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and medical history. This approach ensures that patients receive treatments tailored to their specific needs, improving the effectiveness of care.
3. Digital Health Records: Streamlining Patient Information
The digitization of health records has been a game-changer in India’s healthcare transformation. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) are replacing paper-based systems, leading to improved patient care, better data management, and enhanced interoperability.
– Seamless Data Access: Digital health records allow healthcare providers to access a patient’s medical history, lab results, and treatment plans in real time, leading to more informed and accurate diagnoses. This is particularly important during emergencies when timely access to patient information can be life-saving.
– Government Initiatives: The Indian government launched the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) to create a unified digital health ecosystem. Through ABDM, citizens can create unique health IDs that link to their medical records, making it easier for healthcare providers to access and share patient information across different facilities.
– Data Security: With the rise of digital health records, ensuring data privacy and security has become paramount. Healthcare institutions are increasingly adopting secure cloud-based systems and encryption technologies to protect sensitive patient information.
4. Wearable Devices and Remote Monitoring

Wearable devices, such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and medical monitoring devices, are revolutionizing how healthcare is delivered in India. These devices enable continuous monitoring of vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels, empowering patients to take control of their health.
– Chronic Disease Management: Wearable devices are particularly useful for managing chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. Patients can monitor their health parameters in real-time and share the data with healthcare providers, enabling timely interventions and reducing the risk of complications.
– Preventive Healthcare: Wearables encourage preventive healthcare by promoting physical activity, tracking sleep patterns, and monitoring overall fitness levels. This helps individuals stay proactive about their health and make lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
– Remote Monitoring: Remote patient monitoring systems are becoming increasingly popular, allowing healthcare providers to track a patient’s condition from a distance. For example, patients recovering from surgery or managing chronic illnesses can use wearable devices to send real-time data to their doctors, ensuring that any abnormalities are detected early.
5. Mobile Health (mHealth) Apps: Empowering Patients

The widespread use of smartphones in India has paved the way for the rapid adoption of mHealth apps, which provide users with a range of healthcare services at their fingertips.
– Access to Information: mHealth apps offer a wealth of information on various health topics, from disease prevention to mental health and fitness. These apps empower users to educate themselves about their health and make informed decisions.
– Appointment Scheduling and Medication Reminders: Many healthcare apps allow patients to schedule appointments, receive reminders for medication, and track their health progress. Due to this administration work load gets lessen on medical person lead to better care on patients.
– Mental Health Support: Mental health apps are gaining popularity in India, providing users with access to counselling services, mindfulness exercises, and mental health resources. These apps are helping reduce the stigma around mental health and making mental healthcare more accessible.
6. Robotics and Automation: Improving Precision in Surgery

Robotics is making a significant space in medicine sector. As, robotic surgery offers higher precision, reduces recovery time, and minimizes the risk of complications.
– Minimally Invasive Surgeries: Robotic systems enable surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy, leading to less invasive surgeries and faster recovery times.
– Automation in Hospitals: Automation is also streamlining various hospital processes, from drug dispensing to inventory management. Automated systems improve efficiency, reduce human errors, and ensure that critical resources are available when needed.
7. Government Initiatives: Driving Technology Adoption

The Indian government has been instrumental in promoting the use of technology in healthcare through various initiatives aimed at improving access, affordability, and quality of care.
– Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY): This ambitious health insurance scheme aims to provide financial protection to over 500 million people in India.
– National Digital Health Blueprint: it outlines India’s roadmap for creating a digital healthcare ecosystem. It emphasizes the use of telemedicine, health apps, and digital records to improve healthcare delivery.
– Arogya Setu App: During the COVID-19 pandemic, the Indian government launched the Arogya Setu mobile app to track the spread of the virus, provide real-time updates, and offer teleconsultations to users.
8. Challenges and the Way Forward
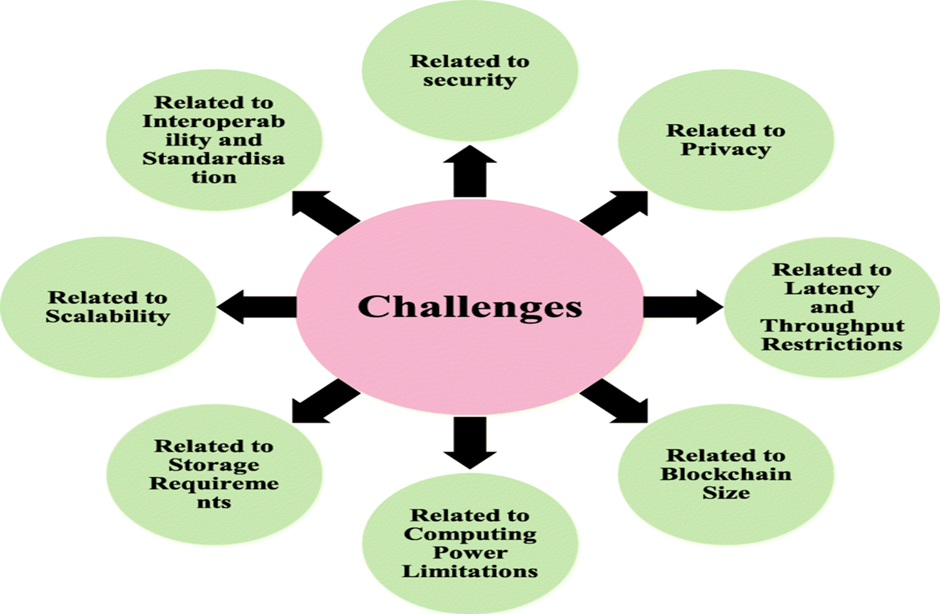
While technology is transforming India’s healthcare system, several challenges remain:
– in remote areas, people face difficulty due to lesser internet connectivity.
-the digital literacy is poor in some of the regions.
– With the increasing digitization of health records raises concerns about data privacy and security.
– Healthcare professionals need training to effectively use new technologies such as AI, robotics, and digital health records. Continuous education and upskilling programs will be crucial in maximizing the potential of technology in healthcare.
– While technology has the potential to make healthcare more accessible, affordability remains a concern for a large portion of the population. The government and private sector must work together to ensure that technological innovations are affordable and accessible to all.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.